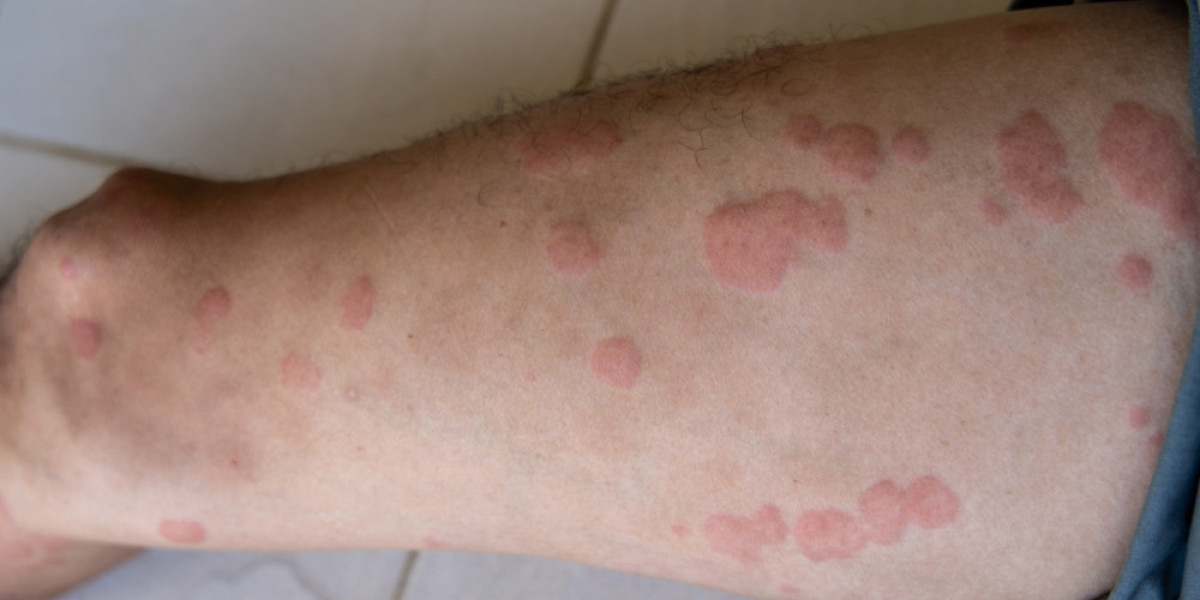
Chronic urticaria is a skin condition that causes persistent hives lasting longer than six weeks. These red, swollen, and itchy welts can appear anywhere on the body and often change shape, size, and location. Unlike acute urticaria, which usually results from an allergic reaction, chronic urticaria has no clear cause in many cases.
For some, chronic urticaria comes and goes without any obvious triggers. Others experience it as part of an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. It can also be linked to infections, stress, or underlying medical conditions like thyroid disease or lupus.
Beyond the physical discomfort, chronic urticaria can affect mental health. Constant itching and unpredictability can lead to anxiety, stress, and sleep disturbances. If your hives are interfering with daily life, it may be time to consider medical intervention or urticaria research trials to help find potential treatments.
Common Triggers: What Could Be Causing Your Symptoms?
Chronic urticaria often develops without a clear trigger, but certain factors can make symptoms worse. Identifying what might be causing your flare-ups is an important step in managing the condition.
Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Some people react to certain foods (nuts, shellfish, dairy), pet dander, pollen, or dust mites.
- Temperature changes: Heat, cold, or sudden temperature shifts can trigger hives.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional distress can worsen symptoms, even if there’s no physical cause.
- Infections and illnesses: Viral infections, bacterial infections (like H. pylori), or underlying conditions can contribute.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis have been linked to chronic urticaria.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and some blood pressure medications can trigger hives.
While avoiding triggers can help, it’s not always easy to pinpoint the cause. If your hives keep returning despite lifestyle changes, a doctor can help determine if an underlying condition is at play.
Signs That It’s Time to See a Doctor
You might be wondering: “At what point should I stop waiting for my hives to disappear and see a doctor?” While occasional flare-ups are normal, persistent symptoms may indicate a bigger issue.
Signs that warrant medical attention include:
- Hives lasting more than six weeks – If your symptoms persist despite home remedies, professional evaluation is necessary.
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema) – This could be a sign of a more serious allergic reaction.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing – This requires immediate medical attention as it may indicate anaphylaxis.
- Frequent recurrences despite antihistamines – If over-the-counter medications aren’t working, stronger treatments may be needed.
- Impact on sleep or daily activities – If your hives are affecting your work, social life, or mental well-being, it’s time to seek help.
- Signs of an underlying condition – Fatigue, joint pain, or weight changes could indicate autoimmune disease or another systemic issue.
Ignoring these signs can lead to worsening symptoms and unnecessary suffering. A healthcare provider can help identify the cause and offer treatments tailored to your needs.
What to Expect During a Doctor’s Visit
Seeing a doctor for chronic urticaria doesn’t have to be overwhelming. In fact, a simple consultation can set you on the right path toward relief.
Here’s what typically happens during an appointment:
- Medical history review – Your doctor will ask about symptom duration, possible triggers, and any related conditions.
- Physical examination – They’ll check your skin and look for signs of underlying issues.
- Allergy testing (if applicable) – In some cases, blood or skin tests may be performed to rule out allergies.
- Blood tests – To check for autoimmune diseases, infections, or thyroid disorders.
- Symptom tracking discussion – You may be asked to keep a journal of when your hives appear and what you were doing before they occurred.
Knowing what to expect can make the process easier. Keeping a record of your symptoms beforehand can also help your doctor pinpoint potential triggers and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment Options for Chronic Urticaria
The right treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms and whether there’s an underlying cause.
Common treatment options include:
- Antihistamines – These are the first line of defense, helping to block histamine, the chemical responsible for hives.
- Corticosteroids – Short-term use of steroids can help reduce inflammation for severe cases.
- Immunosuppressants – Medications like cyclosporine may be prescribed if antihistamines aren’t enough.
- Biologics (omalizumab/Xolair) – A targeted injection that blocks allergic reactions and is approved for chronic urticaria.
- Lifestyle changes – Avoiding triggers, reducing stress, and following an anti-inflammatory diet may help.
Since no single treatment works for everyone, it often takes some trial and error. If standard therapies fail, exploring advanced options like clinical trials may be beneficial.
Can Urticaria Clinical Research Trials Help?
If traditional treatments aren’t working, urticaria clinical research trials might be an option. These trials test new medications and therapies that aren’t yet widely available but could offer more effective solutions.
Why consider a clinical trial?
- Access to cutting-edge treatments.
- Closer medical supervision from specialists.
- Potential for long-term symptom relief.
Many people hesitate to join clinical trials due to safety concerns, but these studies follow strict guidelines to ensure participant well-being. If you’re struggling with chronic urticaria and haven’t found relief, asking your doctor about available trials could open new doors to effective treatment.
Conclusion: Living With Exercise-Induced Urticaria
Chronic urticaria can be unpredictable, frustrating, and exhausting. However, knowing when to seek medical help is crucial for finding relief. If your hives are persistent, severe, or affecting your quality of life, a doctor can help identify the right treatment.
For those living with exercise-induced urticaria, working with a doctor to develop a safe workout plan can help manage symptoms without giving up physical activity.
If you’re tired of struggling with chronic hives, don’t wait—schedule a consultation today and explore all available treatment options, including clinical trials, to take control of your health.